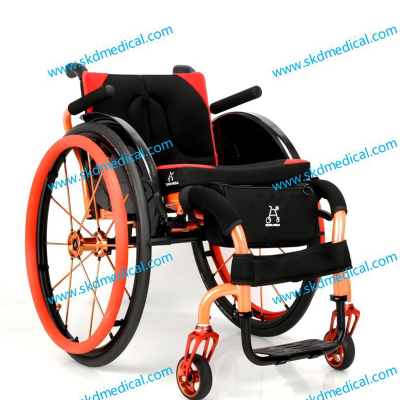
What kind of disease diagnosis is suitable for wheelchair use?
2024-09-19 15:30
As an important walking aid, wheelchairs provide great convenience and independence for patients with limited mobility. However, what kind of disease diagnosis is suitable for wheelchair use? This question involves multiple medical fields, including neurology, orthopedics, cardiology, and geriatrics.
This article will analyze in depth the various disease diagnoses that are suitable for wheelchair use, explore their causes and specific needs, and help patients and their families better understand and choose appropriate assistive tools.

What kind of disease diagnosis is suitable for wheelchair use?
Diseases suitable for wheelchair use: neurological diseases
Neurological diseases are one of the main causes of patients' mobility difficulties. These diseases often affect patients' muscle control, balance, and coordination, making it difficult for them to walk independently. Neurological diseases include: spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson's disease.
Spinal cord injury:
Spinal cord injury (SCI) refers to damage to the spinal cord function caused by trauma or disease, resulting in partial or complete loss of movement and sensory function of the body. Patients with spinal cord injuries may need to use wheelchairs for a long time or permanently to assist mobility, depending on the site and severity of the injury.
● Cause: Trauma (such as car accidents, falls), tumors, infections, etc.
● Needs: High-back wheelchairs, manual or electric wheelchairs, tilt wheelchairs, etc., choose different types of wheelchairs according to the location and degree of injury.
Multiple Sclerosis:
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that causes damage to the myelin sheath of the central nervous system, affecting the normal function of the brain and spinal cord. Patients often experience muscle weakness, coordination disorders and balance problems.
● Cause: Autoimmune reaction.
● Needs: Lightweight wheelchairs, electric wheelchairs, support wheelchairs, etc., choose different types of wheelchairs according to the progression of the disease.
Parkinson's Disease:
Parkinson's Disease is a common neurodegenerative disease that mainly affects the patient's motor function. Symptoms include tremor, muscle stiffness, bradykinesia and unstable posture.
● Cause: Loss of dopamine neurons.
● Needs: Manual wheelchairs, electric wheelchairs, stable wheelchairs, etc., to help patients maintain mobility when their motor function is limited.
Diseases suitable for wheelchair use: Orthopedic diseases
Orthopedic diseases are also common reasons why patients need to use wheelchairs. These diseases usually affect bones, joints and muscles, making it impossible for patients to walk normally. Orthopedic diseases include: fractures, osteoarthritis, congenital bone diseases, etc.
Fractures:
Severe fractures, especially fractures of the hip, spine and lower limbs, may cause patients to temporarily or permanently lose the ability to walk. During recovery or in the case of severe injuries, wheelchairs become necessary auxiliary tools.
● Causes: trauma, falls, car accidents, etc.
● Demand: temporary manual wheelchairs or electric wheelchairs to help patients stay active during recovery.
Osteoarthritis:
Osteoarthritis is a common chronic joint disease that causes joint pain, stiffness and limited mobility. Severe osteoarthritis may affect patients' ability to walk and require the use of wheelchairs.
● Causes: joint wear, inflammation, genetic factors, etc.
● Demand: comfortable wheelchairs, wheelchairs with good shock absorption function, to relieve joint pressure and pain.
Congenital bone diseases:
Some congenital bone diseases, such as Osteogenesis Imperfecta and Scoliosis, can cause bone deformity and fragility, making it difficult for patients to walk independently.
● Cause: Genetic mutation.
● Demand: Special wheelchairs, support wheelchairs, customized according to the specific needs and physical condition of the patient.

Diseases suitable for wheelchairs: Heart and respiratory diseases
Heart and respiratory diseases may cause patients to lose strength and have difficulty breathing, affecting their walking ability and endurance. Heart and respiratory diseases include: heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc.
Heart failure:
Heart failure is a serious heart disease that causes the heart to be unable to pump blood effectively, causing patients to be extremely tired and have difficulty breathing. Wheelchairs can help patients save energy and reduce the burden on the heart.
● Cause: Coronary heart disease, hypertension, cardiomyopathy, etc.
● Demand: Lightweight wheelchairs, electric wheelchairs, to help patients maintain mobility when they are tired.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common chronic respiratory disease that causes breathing difficulties and physical decline. Wheelchairs can help patients maintain mobility when they are physically weak.
● Causes: smoking, air pollution, occupational exposure, etc.
● Demand: lightweight wheelchairs, electric wheelchairs, to help patients maintain mobility when they have difficulty breathing.
Diseases suitable for wheelchairs: geriatric diseases
As they age, the elderly often face a variety of chronic diseases and physical decline, which affect their ability to walk. Geriatric diseases include: Alzheimer's disease, osteoporosis, etc.
Alzheimer's disease:
Dementia is a chronic disease that affects memory, thinking and behavior, causing patients to gradually lose their ability to live independently. Wheelchairs can help patients with senile dementia maintain mobility when they have difficulty moving.
● Causes: Alzheimer's disease, cerebrovascular disease, etc.
● Demand: safety wheelchairs, comfortable wheelchairs, to help patients move in a safe and comfortable environment.
Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is a common disease in the elderly that causes bones to be fragile and prone to fractures. Patients recovering from fractures or with severe osteoporosis may need to use a wheelchair.
● Causes: calcium loss, hormone changes, genetic factors, etc.
● Demand: temporary use of manual or electric wheelchairs to help patients stay active during recovery.
Other causes
Trauma:
Severe trauma, such as car accidents, falls, etc., may cause multiple fractures or severe soft tissue damage, making it impossible for patients to walk. Wheelchairs become necessary auxiliary tools during recovery or in the case of permanent disability.
● Causes: accidents, sports injuries, etc.
● Demand: temporary or long-term use of manual or electric wheelchairs to help patients stay active during recovery.
Recovery after surgery:
After some major surgeries, patients need to stay in bed for a long time to gradually regain the ability to walk. Wheelchairs can help patients stay active during the recovery period and avoid complications caused by long-term bed rest.
● Causes: joint replacement surgery, spinal surgery, etc.
● Need: A manual or electric wheelchair for temporary use to help patients stay mobile during recovery.

Conclusion
In summary, the disease diagnoses suitable for wheelchair use include neurological diseases (such as spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease), orthopedic diseases (such as fractures, osteoarthritis and congenital bone diseases), cardiac and respiratory diseases (such as heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), geriatric diseases (such as Alzheimer's disease and osteoporosis), and other reasons (such as severe trauma and post-operative recovery).
Different disease diagnoses require different types of wheelchairs to meet the specific needs of patients. Choosing the right wheelchair can not only improve the patient's quality of life, but also facilitate the rehabilitation process and reduce the burden on caregivers. Understanding the characteristics and needs of these diseases can help patients and their families make more informed decisions and choose the most suitable assistive tools.