What are the dimensions of a hospital bed?
2024-11-21 15:30
In a hospital setting, a bed is not only a place for patients to rest and receive treatment, but also a workstation for doctors and nurses to provide treatment and care. Therefore, understanding the dimensions of a hospital bed and its importance is essential to ensure comfortable, safe and effective care for patients. This article will delve into the different dimensions of hospital beds and their significance, and provide you with a comprehensive guide to help you choose the right bed.

What are the different hospital bed dimensions and their importance?
The dimensions of a hospital bed directly affect the comfort of the patient, the ease of operation for caregivers, and the configuration of medical equipment. A bed that is too small may limit the patient's space for movement, increase mattress pressure, and cause problems such as bedsores. An oversized bed may take up too much space in the ward and affect the placement of other medical equipment. Therefore, choosing the right bed size is crucial.
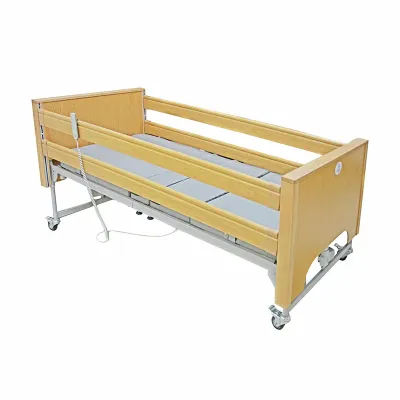
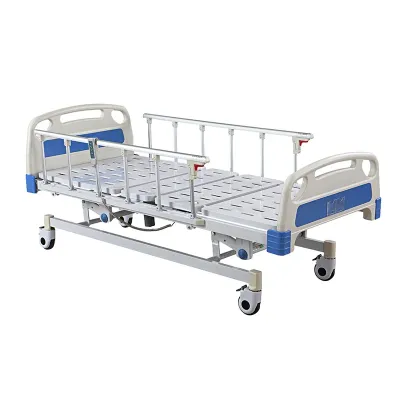
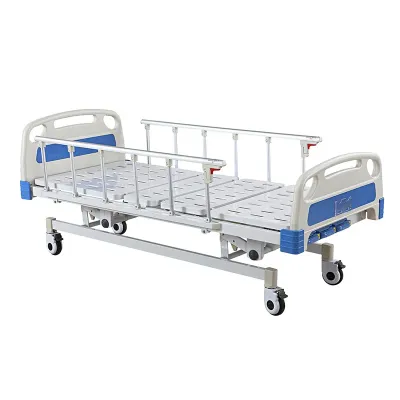
The dimensions of a hospital bed include length, width, and height. These dimensions determine the patient's range of movement in bed and also affect the ease with which caregivers can perform operations such as position changes and transfers. The width of a hospital bed is usually between 91 cm (36 inches) and 107 cm (42 inches), while the length is mostly between 191 cm (75 inches) and 213 cm (84 inches).
What are the standard dimensions of a hospital bed?
The dimensions of a standard hospital bed are usually 91 cm wide and 203 cm long, with an adjustable height, usually between 38 cm and 76 cm. This size can meet the needs of general adult patients in most cases, and it is also convenient for nursing staff to perform nursing operations. However, standard sizes are not suitable for all patients, and different sizes of beds are required in special cases.
For patients with smaller stature or limited mobility, standard beds may be too large or not flexible enough, and for obese patients, standard beds may not provide enough support. Therefore, hospitals usually choose the appropriate bed size according to the specific situation of the patient.
● Standard hospital bed: Standard beds are usually designed to accommodate most adult patients, with a width of about 91 cm (about 36 inches) and a length of 191 cm (about 75 inches) to 203 cm (about 80 inches). Such a size can provide enough space for activities and is convenient for medical staff to operate.
● Children's hospital beds: Children's beds are usually smaller in size to accommodate children's physical needs. The standard children's hospital bed is about 71 cm (about 28 inches) wide and 142 cm (about 56 inches) long. These beds are also designed with guardrails for increased safety.
● Intensive care beds (ICU beds): Intensive care beds are usually designed to be wider than ordinary beds to accommodate more medical equipment and monitoring devices. The width is about 102 cm (about 40 inches) to 122 cm (about 48 inches), and the length is usually around 203 cm (about 80 inches).
How is the size of a bariatric bed different from that of an ordinary hospital bed?
Bariatric beds, as the name suggests, are designed for obese or heavier patients. The size of this type of bed is usually larger, with a width of generally between 122 cm (48 inches) and 152 cm (60 inches), and a length of up to 213 cm (84 inches). In addition, the weight-bearing capacity of bariatric beds is also much higher than that of standard beds, and can usually carry up to 450 kg or even more.
The design of bariatric beds takes into account not only the patient's weight, but also the difficulty of operation for caregivers during transfer and care. The spacious bed surface and sturdy structure can effectively reduce the patient's discomfort while reducing the risk of caregivers during operation.

Are there bed sizes for pediatric patients in the hospital?
The size of pediatric beds is usually smaller to accommodate the body shape and special needs of children. Generally speaking, the width of pediatric beds ranges from 61 cm to 76 cm, and the length ranges from 122 cm to 152 cm. These beds are usually equipped with fences to prevent children from falling from the bed, and it is also convenient for caregivers to care for children.
The design of pediatric beds takes into account the special needs of children's mobility and care, such as more flexible height adjustment, softer mattresses, etc. In addition, many pediatric beds are also equipped with fun patterns and colors to relieve children's anxiety and fear.
For taller patients, can the length of hospital beds be adjusted?
For taller patients, a standard-length hospital bed may be too short, making it difficult for the patient to stretch out in the bed. To address this, many hospitals offer extended beds that can be extended to 213 cm (84 inches) or longer. In addition, some beds are equipped with a foot extension device to further increase the length of the bed when needed.
This adjustable design not only increases patient comfort, but also facilitates nursing staff to operate. For example, when performing position adjustments, transfers, or other nursing operations, the additional length provides more room for operation and reduces patient discomfort.
What is the weight capacity of a typical hospital bed?
The weight capacity of a hospital bed is a critical parameter that is directly related to patient safety. A typical hospital bed can usually carry a weight of about 250 kg (about 550 pounds), which is sufficient for most adult patients. However, for patients who weigh more than the standard range, such as obese patients, a specially designed bariatric bed may be required. These beds can have a weight capacity of 450 kg or more to ensure patient safety and comfort.
The load-bearing capacity of a hospital bed depends not only on the material and structure of the bed frame, but also on the design of the mattress. In order to ensure the safety of patients, hospitals will strictly evaluate the patient's weight and physical condition when selecting a hospital bed to ensure that the bed can provide sufficient support.

How do you choose the size of bed you need?
Choosing the right bed size requires considering multiple factors, including the patient's physical condition, nursing needs, ward space, and the configuration of other medical equipment. When choosing a hospital bed, the patient's height, weight, and physical mobility should be evaluated first. If the patient is taller or heavier, a longer or wider bed may be required.
In addition, the patient's nursing needs are also an important factor in choosing the size of the bed. For example, if the patient needs to frequently change position or transfer operations, a wider bed can provide more operating space and reduce the patient's discomfort. At the same time, if the ward space is limited, choosing a smaller bed can save space and facilitate the placement of other equipment.
What are the dimensions of a hospital mattress?
The dimensions of a hospital mattress usually match the dimensions of the bed to ensure the comfort and safety of the patient. The dimensions of a standard hospital mattress are 91 cm (36 inches) wide, 191 cm (75 inches) long, and 10 to 15 cm (about 4 to 6 inches) thick. For bariatric or pediatric beds, the dimensions of the mattress will vary accordingly to accommodate different types of beds.
The choice of mattress depends not only on its size, but also on its material and design. High-quality hospital mattresses usually use antibacterial, waterproof and breathable materials to ensure patient hygiene and comfort. In addition, the hardness and support of the mattress are also important factors affecting patient comfort and should be selected according to the specific needs of the patient.