How Can Hospital Beds Help Stroke Recovery?
2024-10-23 15:30
Stroke is a sudden illness that usually occurs without warning and has a significant impact on the patient's health and quality of life. After a stroke, patients may face a long recovery process, and hospital beds play a vital role in this process.
This article will explore in detail what stroke is, common symptoms of stroke, treatment methods and risk factors, and focus on how hospital beds can help stroke patients in their recovery process.

What is a stroke?
A stroke, also known as a cerebral infarction, is an interruption of blood supply to the brain, causing brain cells to die rapidly due to lack of oxygen. Strokes can be divided into two major categories: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. Ischemic stroke is the most common type, accounting for about 87% of all stroke cases. It is usually caused by a blood clot or hardening of the arteries, which blocks blood flow to the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a ruptured blood vessel in the brain, causing blood to leak into brain tissue and cause serious damage.
Stroke is an emergency and must be acted upon quickly after symptoms appear, because the golden time for treatment is only a few hours. Delaying treatment can lead to irreversible brain damage or even death.
What are the common symptoms of a stroke?
The symptoms of a stroke vary from person to person, depending on where in the brain the damage is and how severe it is. Here are some common symptoms of a stroke:
● Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arms, or legs, especially when it occurs on one side of the body. The patient may be unable to lift their arms or control facial muscles, causing one side of the face to droop.
● Difficulty speaking. The patient may suddenly be unable to speak, or their speech may be slurred and difficult to understand. Speech disorders are an important sign of a stroke.
● Blurred or lost vision. A stroke may cause sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes, or even double vision.
● Sudden headache. Severe headaches, especially those accompanied by vomiting, dizziness, or loss of consciousness, may be a sign of a hemorrhagic stroke.
● Unsteady gait or loss of balance. The patient may suddenly feel dizzy, have an unsteady gait, or lose coordination.
Is there a cure for stroke?
Stroke is a serious disease, and while there is no complete cure, early intervention and ongoing rehabilitation can improve the patient's quality of life. For ischemic stroke, thrombolytic therapy (drugs that dissolve blood clots) can significantly reduce the extent of brain damage when given within hours of onset. For hemorrhagic stroke, surgery may be necessary to repair ruptured blood vessels and reduce pressure on the brain.
However, the recovery process after a stroke is often long and complicated. Rehabilitation therapy, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, are important components of stroke rehabilitation. The goal of rehabilitation is to help patients relearn and regain skills lost due to stroke, such as the ability to walk, talk, and perform daily activities independently.
Who is at risk for stroke?
The occurrence of stroke is often associated with a variety of risk factors, including controllable lifestyle habits as well as uncontrollable physiological conditions. Here are some of the main risk factors for stroke:
● High blood pressure: Long-term uncontrolled high blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke. It increases the risk of hardening of the arteries and can cause blood vessels to rupture or clots to form.
● Smoking: Smoking causes narrowing of blood vessels and hardening of the arteries, increasing the risk of stroke.
● Diabetes: People with diabetes are prone to blood vessel damage, increasing the chance of stroke.
● High cholesterol: High cholesterol levels can promote hardening of the arteries, which increases the risk of stroke.
● Heart disease: Heart disease, especially atrial fibrillation, can cause blood clots to form, increasing the likelihood of stroke.
● Family history: If someone in your family has had a stroke, the risk for other members is also increased.
● Age and gender: The risk of stroke increases with age, and the risk is higher for people over 55 years old. In addition, men are at a higher risk of stroke at an early age than women, but women have a higher mortality rate from stroke.
What are the early symptoms of stroke?
Identifying the early symptoms of stroke is crucial to getting timely treatment. The American Stroke Association recommends using the "FAST" method to identify signs of stroke:
● F (Face): Facial droop. Ask the patient to smile and observe whether one side of the face droops.
● A (Arms): Arm weakness. Ask the patient to raise both arms to see if one arm cannot be raised or balanced.
● S (Speech): Speech difficulties. Ask the patient to repeat a simple sentence and listen for slurred speech.
● T (Time): Act in time. If you observe the above symptoms, call 911 immediately for help.
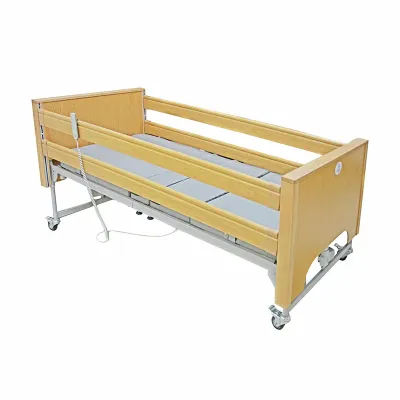
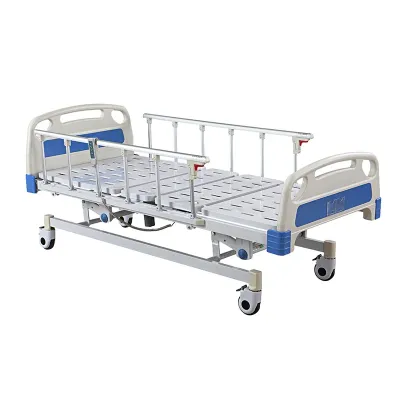
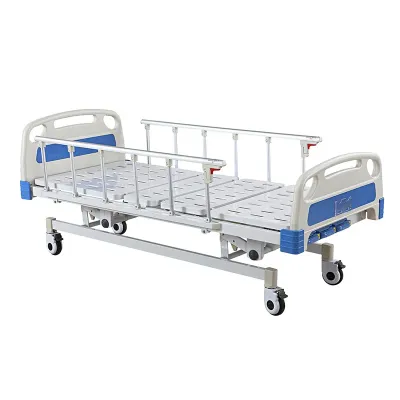
What are hospital beds and how are they used for stroke recovery?
A hospital bed is a bed designed specifically for hospitalized patients that has a variety of features that can be adjusted to the patient's needs. These beds are usually equipped with an electric adjustment system that can adjust the height of the bed and the angle of the head and foot of the bed, helping to provide the patient with optimal comfort and ease of care.
For stroke patients, hospital beds play an irreplaceable role in the recovery process. After a stroke, patients often need to stay in bed for a long time, which can lead to a series of problems such as bedsores, muscle atrophy, and poor circulation. Hospital beds can help alleviate these problems and promote patients' recovery by providing a variety of features.
How do hospital beds help stroke patients' mobility?
Stroke patients usually experience weakness or paralysis on one side of the body after the onset of the disease, which makes them unable to move independently or perform daily activities. The various adjustment features of hospital beds can help patients regain some mobility:
Headline lift function
The headline lift function of hospital beds allows patients to easily adjust to a sitting position, which helps with daily activities such as eating, reading, and communicating with family members. The height adjustment of the head of the bed can also help patients with physical therapy and promote muscle activity in the upper body.
Height adjustment
The height adjustment function of hospital beds is an important design for both caregivers and patients. The height adjustment can facilitate patients' mobility in bed, reduce the difficulty of getting in and out of the bed, and reduce the physical stress of caregivers when operating.
Transfer support
Some hospital beds are equipped with lateral tilt functions or additional transfer aids to help stroke patients transfer to wheelchairs or other seats more easily. These features are essential to promote patient independence and reduce caregiver fatigue.

Can hospital beds help prevent bedsores in stroke patients?
Prolonged bed rest is one of the main causes of bedsores. Stroke patients are more susceptible to bedsores due to their limited mobility. Hospital beds play a significant role in preventing and reducing bedsores:
Adjustable bed surface
The adjustable bed surface of hospital beds can help patients change their posture regularly and relieve local pressure, thereby reducing the risk of bedsores. Adjustment of the head, foot and overall height of the bed can help patients maintain different body postures and avoid applying pressure to the same part for a long time.
Special mattresses
Many hospital beds are equipped with pressure-relieving mattresses, which are specially designed to disperse body pressure and promote blood circulation. Air mattresses, foam mattresses, and gel mattresses are common choices that can effectively prevent the formation of bedsores.
Turning assistance
Some high-end hospital beds have automatic turning functions, which can help patients change positions at regular intervals, reduce the workload of caregivers, and effectively prevent the occurrence of bedsores.
How do hospital beds help stroke patients stay safe?
Stroke patients often face a series of safety issues, especially when trying to move or get out of bed alone. Hospital beds help reduce risks and ensure patient safety through a variety of safety designs.
Guardrail design
Hospital beds are often equipped with guardrails to prevent patients from accidentally falling. The height and position of the guardrails can be adjusted as needed to provide maximum protection. In addition, the guardrails can help patients get support when moving, reducing the possibility of falling.
Emergency alarm system
Many hospital beds are equipped with emergency alarm systems, so patients can quickly call caregivers when they need help. This feature is especially useful for stroke patients, who may not be able to shout loudly when they need help.
Anti-slip surface
Hospital beds often have anti-slip materials on their mattresses and surfaces to reduce the risk of patients slipping when moving in bed. This design detail can greatly improve patient safety.
How do stroke patients and their caregivers choose the right bed?
Choosing the right hospital bed is an important step in the recovery process for stroke patients. Here are some tips to help patients and their caregivers make an informed choice:
Choose features based on patient needs
Different patients have different needs, and some patients may need more complex adjustment features, such as independent control of bed height, head and foot angles. Other patients may need lateral tilt or automatic turning functions. Choosing the right bed features based on the patient's recovery needs can help them recover better.
Consider the size of the bed
The size of the hospital bed should also be selected based on the patient's physical condition. The length, width, and height of the bed need to accommodate the patient's height, weight, and mobility. A bed that is too small may cause discomfort to the patient, while a bed that is too large may be difficult to care for.
Pay attention to mattress selection
The right mattress is key to preventing bedsores and improving comfort. Stroke patients often need a mattress with pressure relief functions, which can effectively disperse body pressure and promote blood circulation.

What additional features are you looking for in a hospital bed for stroke recovery?
Beyond basic adjustment features, some additional features can significantly improve the stroke patient's recovery experience:
● Remote control: A remote control device allows patients to adjust the bed without relying on caregivers, enhancing independence.
● Memory function: Some hospital beds have a memory function that can save the patient's most commonly used bed settings for quick adjustment.
● Integrated monitoring system: Some high-end hospital beds are equipped with an integrated health monitoring system that can monitor the patient's heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature in real time and automatically transmit data to caregivers.