What is the difference between a transport chair and a wheelchair?
2024-11-27 15:30
In people's daily lives, wheelchairs and transport chairs are two important tools to help people with limited mobility regain mobility. Although they both seem to have the function of helping people move on the surface, there are obvious differences between the two in terms of design, usage scenarios, functions and target users.
This article will explore in detail the main differences between transport chairs and wheelchairs, as well as which type of chair is suitable for which type of user, to help readers better understand how to choose the right mobility aid according to their own or others' needs.
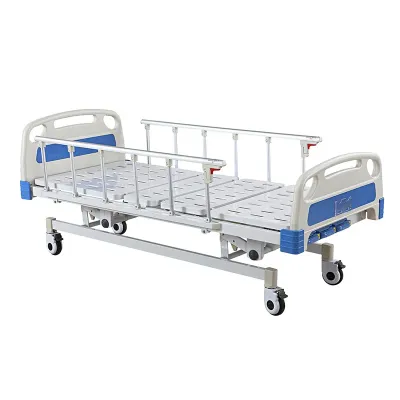
What is a transport chair?
A transport chair, also known as a transfer chair or shift chair, is a lightweight chair designed specifically for short-distance movement. This chair is usually pushed by a caregiver rather than operated by the user. The design features of the transport chair make it more suitable for temporary or short-term use in environments such as hospitals, airports, and shopping malls, rather than for long-term sitting or self-manipulation.
Design and structural features
The design of transport chairs is mainly based on the core of easy carrying and operation, and is usually lighter than a standard wheelchair. They are usually made of aluminum alloy or other lightweight materials, are lightweight and easy to fold, and are convenient for transportation and storage. The wheels of transport chairs are also relatively small, usually 4 to 8 inches in diameter at the rear and front, meaning they need to be pushed by another person to move, and the user cannot push forward by themselves using the wheel rims of the wheelchair.
Due to the lightness and simplicity of transport chairs, they usually lack many of the extra features of traditional wheelchairs, such as adjustable seat height, removable armrests, etc. Therefore, they are relatively limited in comfort and functionality and are mainly used for short-term, short-distance transportation and transfer.
Main use scenarios
Typical use scenarios of transport chairs include patient movement within hospitals or clinics, passenger transfers in airports, and helping people with limited mobility to move short distances at home or in elderly care facilities. For example, when a patient needs to be transferred from a ward to an examination room, a transport chair is an ideal tool that is convenient for caregivers to operate and can complete the task quickly and lightly.
In general, transport chairs are designed for temporary use. They are suitable for short-term mobility needs, not for long-term sitting or relying on it for autonomous movement in daily life.
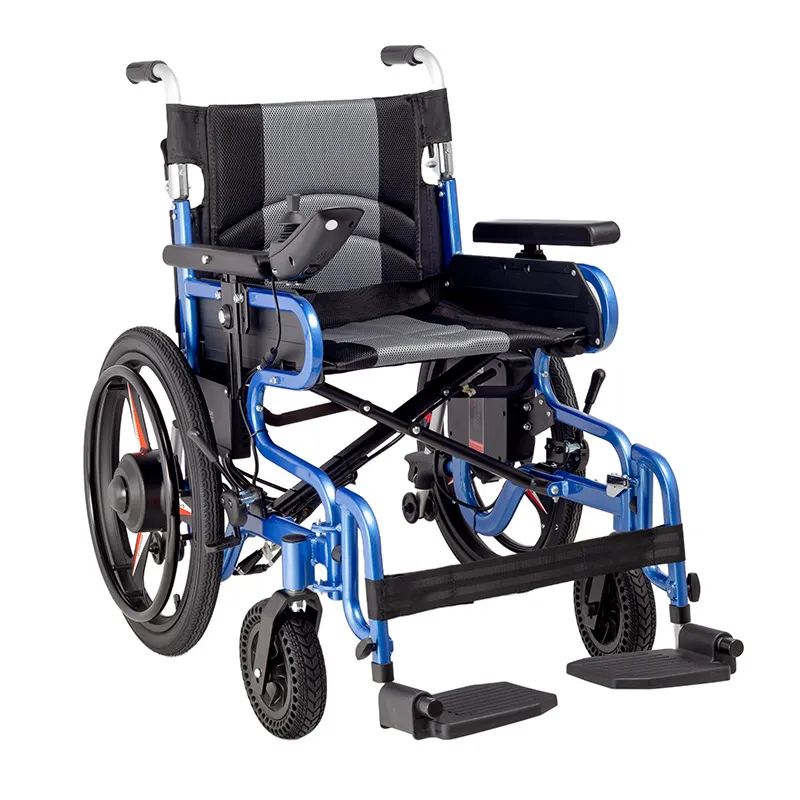

What is a wheelchair?
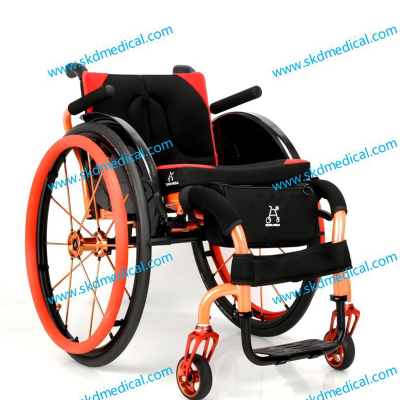
Wheelchairs are assistive devices for people with limited mobility that provide long-term use. They not only help people move freely in indoor and outdoor environments, but also provide users with a high degree of comfort and autonomy. Unlike transport chairs, wheelchair users can operate the wheelchair themselves without the need for others to push it, especially in the case of manual wheelchairs.
Design and structural features
The design of wheelchairs is much more complex and more robust than that of transport chairs. Manual wheelchairs usually have larger rear wheels, usually between 22 and 26 inches, which allows users to move by themselves by pushing the wheel rims. The design of manual wheelchairs allows users to move relatively independently in daily life without the help of others.
In addition, wheelchairs have more options in terms of comfort and functionality than transport chairs. Many wheelchairs come with adjustable seats, removable armrests, leg supports, and head supports to ensure that users remain comfortable during long-term use. For users who need to use them for a long time, the design of the wheelchair takes into account the stability and ergonomics of the seat to reduce the pressure on the body from long-term sitting.
As a more advanced type of wheelchair, electric wheelchairs are powered by electric motors, and users can control the movement of the wheelchair using a control panel or joystick. This wheelchair is suitable for users with extremely limited mobility, or even unable to push a manual wheelchair, providing great independence and convenience.
Main use scenarios
Wheelchairs are mainly used for long-term mobility needs in daily life, especially for users who cannot walk or have difficulty walking. Whether indoors or outdoors, wheelchairs can provide people with limited mobility with great freedom and autonomy. Manual wheelchairs are suitable for users with a certain amount of upper limb strength, while electric wheelchairs provide greater convenience for those who cannot push the wheelchair independently.
For example, for those who are recovering from illness or need wheelchair support due to long-term disability, manual or electric wheelchairs are indispensable tools in their lives. Wheelchairs can not only help them complete daily activities, but also enable them to participate in social activities, travel and work.

What is the difference between a transport chair and a wheelchair?
After understanding the basic characteristics of transport chairs and wheelchairs, we can compare the main differences between the two from multiple angles to help users better understand the different use scenarios and user groups suitable for these two devices.
Lightness and portability
Transport chairs are lighter than wheelchairs and are designed to be easier for caregivers to push, carry and store. Because transport chairs use smaller wheels and lightweight materials, they usually weigh much less than wheelchairs, and most models can be easily folded and put into a car trunk or locker. This lightness makes them particularly suitable for short-distance use and temporary needs, such as patient transfers in medical institutions or helping the elderly to move around the home for a short period of time.
Wheelchairs are relatively heavy because they need to provide more functions and comfort, especially electric wheelchairs, whose built-in batteries and motor systems increase the overall weight. This increase in weight can cause some inconvenience in terms of portability, especially when they need to be folded and carried frequently.
Autonomy vs. Dependence
A key advantage of wheelchairs is their autonomy. Manual wheelchairs can be operated by the user by pushing the wheel rims, while electric wheelchairs allow users to move autonomously through a control panel. This means that wheelchairs are suitable for people who want to maintain a certain degree of independence and can move freely around the home or outdoors without relying on others.
In contrast, the user of a transport chair is completely dependent on others to move around. This chair does not provide the user with the ability to move autonomously, so it is more suitable for those who cannot operate the wheelchair themselves or need the help of a caregiver to move for a short period of time.
Comfort and support
Since transport chairs are designed for short-term and temporary use, they are usually less comfortable and supportive. Transport chairs usually have thin seats and backrests, lack additional padding, and cannot provide users with a comfortable experience when sitting for long periods of time. Their leg support and head support functions are also simple and cannot provide users with sufficient body support.
Wheelchairs are different. Manual and electric wheelchairs usually come with more comfortable cushions, support systems, and even some high-end models offer adjustable backrests, armrests, and footrests. These designs take into account the needs of users who may need to use wheelchairs for long periods of time, minimizing the discomfort or health problems caused by long-term sitting.
Use scenarios
The most common use scenario for transport chairs is short-distance and temporary movement. For example, in hospitals or clinics, transport chairs are used to move patients from one area to another. Similarly, in home care, transport chairs can help caregivers quickly move the elderly or patients from a room to another location. These scenarios usually do not require long periods of sitting or autonomous movement, and the caregiver's push is the most important part of the entire movement process.
Wheelchairs are suitable for longer use and more complex movement needs. Whether it is for daily activities at home or traveling around the city, wheelchairs can provide people with limited mobility with greater flexibility and independence. Therefore, it has a wider range of use scenarios, including daily life, workplace, social activities, etc.
Price difference
Transport chairs are usually cheaper than wheelchairs because they are simpler in design and lack complex functions. Most transport chairs are relatively inexpensive and are an affordable option for those who only need to use mobility aids for a short period of time or occasionally.
The price of wheelchairs varies greatly due to their functions, materials, design and other factors. Manual wheelchairs are usually moderately priced, while electric wheelchairs are relatively expensive due to the inclusion of electric systems and more adjustment functions. Some customized or high-end wheelchairs can even be very expensive, especially when the wheelchair needs to meet specific medical needs.

Which users are suitable for which type of chair?
Based on the above difference analysis, we can provide recommendations for different types of users for their mobility aids.
Users suitable for transport chairs
● People with limited mobility but do not need to sit for a long time: Those who have limited mobility due to temporary injuries or diseases may only need to use transport chairs for a short period of time, such as the rehabilitation period after discharge or short-distance movement in the hospital.
● People who cannot move by themselves and need the help of a caregiver: Since the operation of the transport chair is completely dependent on others to push it, it is particularly suitable for those who cannot move by themselves and need to rely on caregivers.
● Temporary needs during travel: Passengers with limited mobility can use the transport chair to meet temporary travel needs in airports, train stations or other public places.
Suitable for users of wheelchairs
● Users who need long-term sitting: For those who need to rely on wheelchairs for a long time due to chronic diseases, permanent disabilities, etc., manual or electric wheelchairs are better choices because they provide more comfort and support.
● People who want to move independently: The autonomy of manual and electric wheelchairs enables users who want to live independently, participate in social and work activities to better integrate into society and get rid of dependence on others.
● People with specific physical needs: Some users may need additional functions such as tilting seats, adjustable backrests and leg supports, which can be met through customized services of wheelchairs.