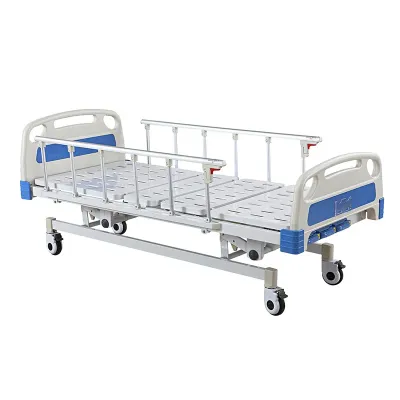
Are hospital beds considered medical devices?
2024-12-09 15:30
Hospital beds may seem commonplace in people's daily lives, but their importance in medical settings cannot be ignored. Are hospital beds considered medical devices? This question seems simple, but it is actually complex. In order to understand this question in depth, we need to first understand what medical devices are, the functions of hospital beds, and their role in healthcare.

Are hospital beds considered medical devices?
The definition of medical devices varies slightly according to the laws and regulations of different countries and regions, but they are generally considered to be devices, tools, or machines used to diagnose, treat, monitor, or prevent diseases. Whether a hospital bed is considered a medical device depends mainly on its function and purpose.
According to the definition of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), medical devices include "devices, tools, devices, instruments, or other articles used for the diagnosis, treatment, prevention, monitoring, mitigation, or compensation of disease or other health conditions." Under this definition, hospital beds, especially those with special functions such as electric adjustment, height adjustment, pressure management system, etc., are clearly classified as medical devices.
In addition, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) also lists hospital beds as a type of medical device, especially those used for nursing, recovery or long-term care. Medical beds often have features that significantly improve patient comfort and support treatment outcomes, thus meeting the standard definition of medical devices.
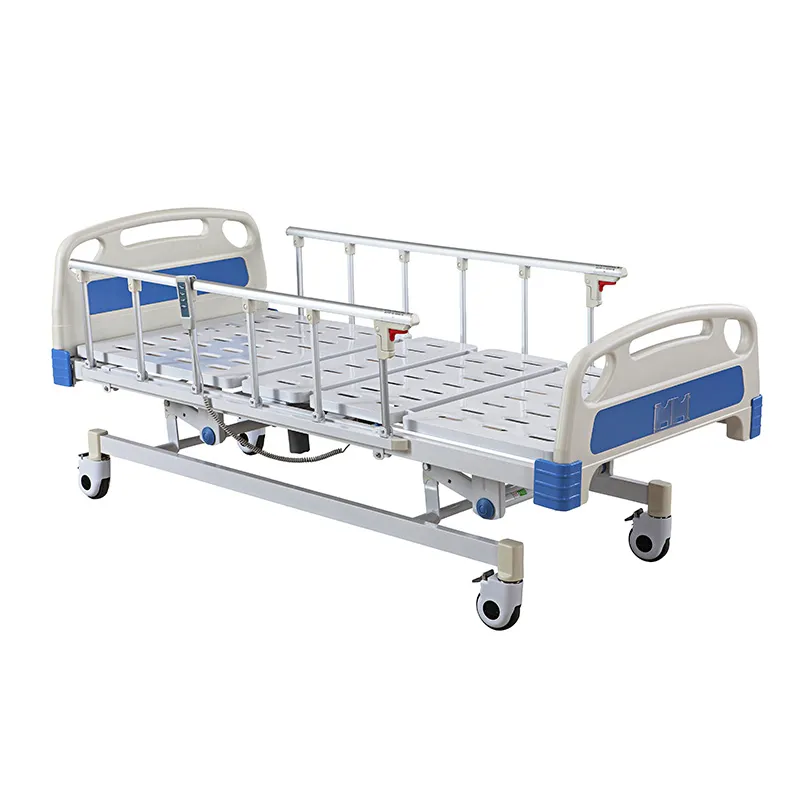

What makes a medical bed different from a traditional bed?
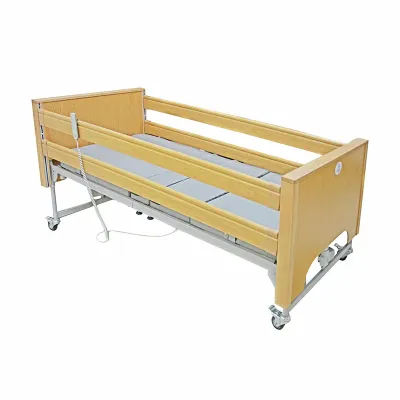
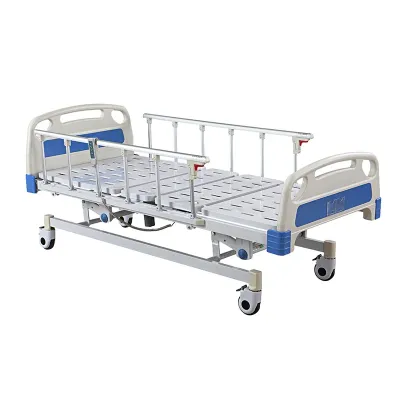
Medical beds are often equipped with an electric system that allows the caregiver or patient to control the height, back and leg tilt angles of the bed with simple controls. This improves comfort and prevents bedsores for bedridden patients. Side rails are also an important component of medical beds, which can effectively prevent patients from falling out of bed, especially for elderly or unconscious patients.
In addition, some medical beds are equipped with advanced pressure management systems that prevent bedsores caused by long-term bed rest by regulating the air pressure of the mattress. Many medical beds are equipped with wheels for easy movement around the room, and have a locking function to ensure that the bed remains stable when needed.
Limitations of traditional beds:
Traditional beds lack the above-mentioned features. Although they are comfortable and practical enough for daily life, they are difficult to meet the requirements of patients who require long-term care or have special medical needs. Therefore, medical beds are considered medical devices because they directly serve the health needs of patients through their design and functionality.
How do I know which medical bed is right for me?
Choosing the right medical bed involves considering many factors, including the patient's health status, care needs, budget, and available space. Start by identifying the specific needs of the patient. For example, does the patient need to be repositioned frequently? Are there special needs to prevent bedsores? Does the patient have cognitive impairment or limited mobility? The answers to these questions can help narrow down your choices.
Choose a bed with features that match the patient's needs. For example, electric adjustment features are particularly important for patients who are bedridden, while an anti-bedsore mattress may be appropriate for patients who need to pay special attention to their skin health.
Medical beds range in price from basic manual beds to high-end fully automatic beds, which can vary by thousands of dollars. Consider your budget range and, if necessary, check with your insurance company to see if some of the costs can be reimbursed. Also, medical beds are usually larger than traditional hospital beds, so make sure there is enough space in your home to accommodate the bed and enough room around it for care and daily use.
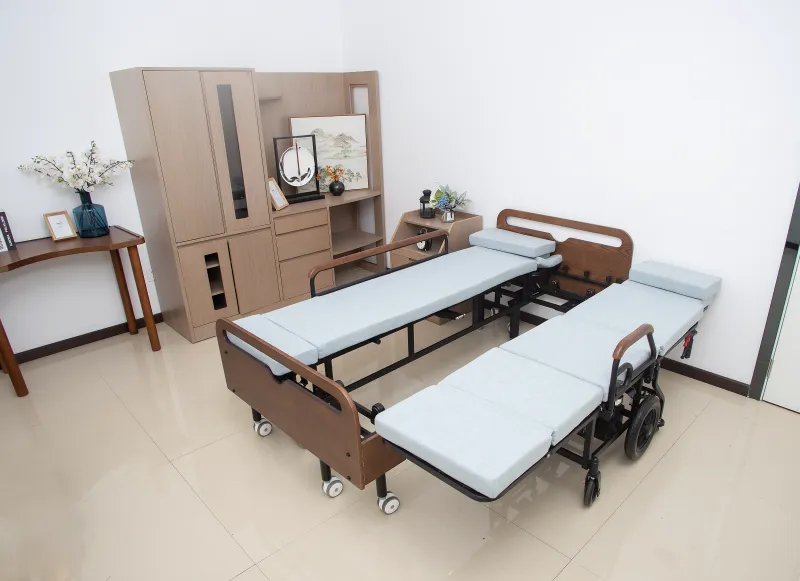
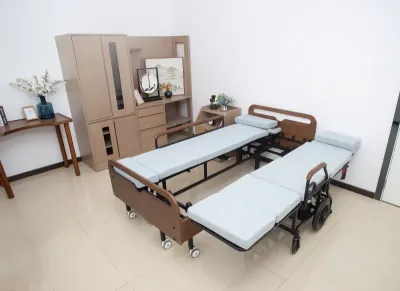
What are some common medical conditions that require a bed at home?
Patients who are bedridden for a long time, recovering from surgery, suffering from chronic diseases, elderly care, and short-term rehabilitation may need to use medical beds at home. The specific explanations are as follows:
● Long-term bedridden: Patients who are bedridden for a long time, such as those with stroke, spinal cord injury, and advanced cancer, usually need medical beds for care and to reduce complications caused by long-term bedridden.
● Postoperative recovery: The recovery period after certain surgeries may require patients to use medical beds at home to adjust their body position, relieve pain, and promote recovery.
● Chronic diseases: Patients with chronic diseases such as heart failure, respiratory diseases, arthritis, etc. may need medical beds to increase comfort and help manage symptoms.
● Elderly care: For elderly people who need long-term care, medical beds can help them spend their later years at home safely and comfortably, while facilitating the work of caregivers.
● Short-term rehabilitation: Even for short-term medical needs, such as recovery from fractures or acute conditions, medical beds can provide the necessary support to help patients recover faster.
Are hospital beds insured?
When buying or renting a hospital bed, many people are concerned about whether insurance can cover the related expenses. In fact, many insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid in the United States, can provide coverage for medical beds for eligible patients.
● Medicare Insurance: In the United States, Part B of Medicare generally covers "Durable Medical Equipment" (DME), which includes medical beds. In order to obtain insurance coverage, the patient's primary physician needs to certify that the bed is necessary for the patient's medical needs and prescribe it accordingly.
● Medicaid Insurance: Medicaid coverage can vary by state, but generally, eligible patients can also obtain medical bed coverage through Medicaid. Similar to Medicare, patients need to provide a doctor's certification, and the equipment must be obtained through a Medicaid-approved supplier.
● Private Insurance: Many private insurance companies also provide coverage for medical beds, but the specific policies vary from insurance plan to insurance plan. Patients need to contact the insurance company directly for specific coverage and conditions.
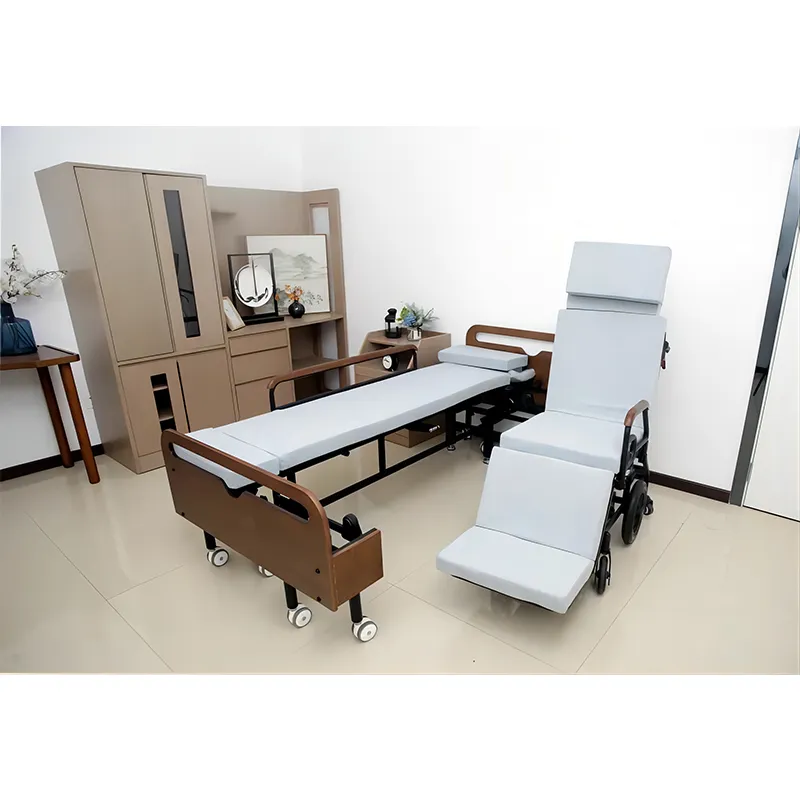

What should I consider when choosing a home hospital bed?
Consider the bed's features, the type of mattress, maintenance and cleaning, whether to rent or buy, whether it is covered by insurance, and the reputation of the supplier.
● Bed functionality: As mentioned above, electric adjustment, pressure management system, side rails, etc. are all important factors to consider. Understand the patient's needs and ensure that the bed has the corresponding functions.
● Mattress type: Medical beds are usually specially designed mattresses that can effectively reduce pressure points caused by long-term bed rest. Memory foam mattresses, air mattresses, etc. are common choices. Choose the right mattress based on the patient's comfort and needs.
● Maintenance and cleaning: Home medical beds require regular maintenance and cleaning to ensure their safety and hygiene. Understand the cleaning requirements of the bed, whether it is easy to disassemble and clean, and whether there are professionals to provide maintenance services.
● Lease or buy: For long-term needs, buying may be a more economical option. For short-term use or families with limited budgets, leasing may be more reasonable. Understand the advantages of each and make a decision after weighing the pros and cons.
● Insurance coverage: As mentioned above, confirm whether the insurance can cover part or all of the expenses, which will affect your final decision.
● Supplier's reputation: It is crucial to choose a reputable supplier. Understand the supplier's service quality and after-sales support to ensure that you can get timely help when you need it.